Beyond The Lithium Era: Exploring the Batteries of Tomorrow
13-Mar-2025

The global battery market has traditionally been led by lithium-ion technology that is fueling devices ranging from smartphones to electric cars and renewable energy storage solutions. Although Li-ion batteries have transformed energy storage their constraints in terms of cost alongside resource availability and energy density have driven research into next-generation battery technologies. The future of energy storage is transitioning to innovative solutions that offer improved efficiency alongside sustainability and superior performance. This blog describes the latest battery technologies with the potential to revolutionize energy industry in the coming years.
The Major Growth Factor
A key factor propelling battery innovation is the swift expansion of the consumer electronics sector. The need for consumer electronics and wearable devices keeps increasing, results in urgent requirement for batteries that offer greater energy density along with quicker charging speeds and extended lifetimes.
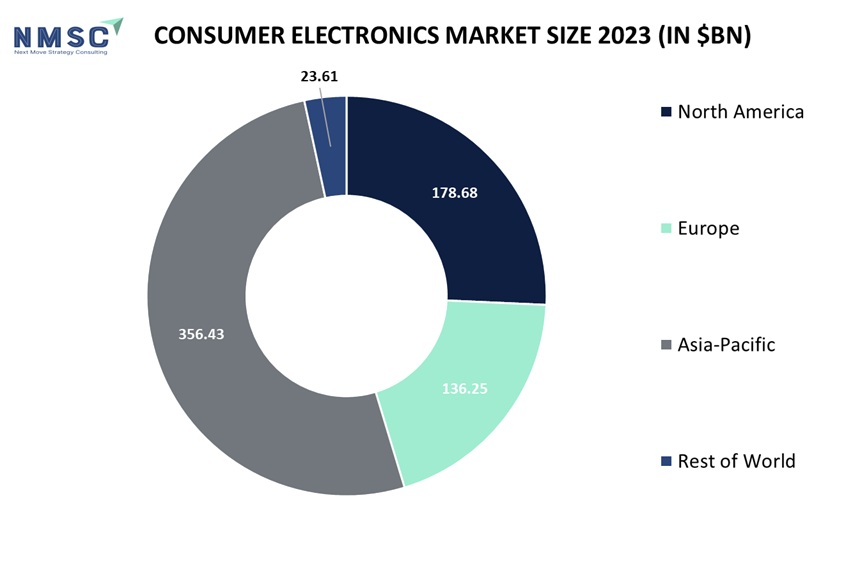
The market for consumer electronics is undergoing significant expansion in various areas. In North America the market is estimated at about USD 178.68 billion whereas Europe comprises roughly USD 136.25 billion. The Asia-Pacific region leads with a market size of USD 356.43 billion that is fueled by robust demand from nations including China, Japan, and India. The rest of world amounts around USD 23.61 billion.
As this market keeps expanding battery producers face mounting pressure to create innovative solutions that can satisfy the changing demands of contemporary electronic devices while prioritizing sustainability and safety.
EXPLORING THE NEXT WAVE OF BATTERY TECH
• Solid-State Batteries
Solid-State batteries represent one of the most promising substitutes for Li-ion technology. These batteries substitute the traditional liquid electrolyte in Li-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte improving safety by removing the danger of fire and explosion. They provide greater energy density allowing for extended battery life in electric vehicles and gadgets, enhanced safety due to non-flammable solid electrolytes and a longer lifespan with diminished degradation over time.
However, obstacles including elevated production expenses along with intricate manufacturing methods and scalability challenges impede large-scale production. Companies such as Toyota and QuantumScape as well as Samsung SDI are leading efforts to commercialize solid-state batteries. Toyota is to introduce solid-state battery for electric cars in a few years while QuantumScape is developing a lithium-metal solid-state battery with significant performance upgrades.

• Sodium-ion batteries
Sodium-ion batteries offer a cost-saving and environmentally friendly option to Li-ion batteries through the utilization of widely available sodium resources, less supply chain risk and environmental exposure. The batteries have stable output in harsh weather conditions and are safer with lower thermal runaway risk. However, their lower energy density is an issue for high-power applications.
To meet this challenge CATL launched second-generation sodium-ion batteries with better energy density and efficiency that is becoming more suitable for EVs and energy storage. At the same time Natron Energy is spending USD 1.4 billion to develop its first U.S. plant in North Carolina to increase production and cope with increasing demand of these batteries. As development and investment continue sodium-ion technology can become formidable in the battery industry especially for cost-constrained and renewable energy applications.
• Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Lithium-sulfur batteries have drawn attention due to their promise to exceed conventional lithium-ion batteries in terms of energy density. Since sulfur is an extremely low-cost and highly available material with the cathode made from sulfur Li-S batteries theoretically hold the capability of up to five times the energy density of Li-ion batteries. This would totally change high energy storage industries such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.

Sion Power developed a lithium-sulfur battery that holds 400% more energy per pound than regular Li-ion batteries. This advance in energy storage capability is extremely attractive to electric vehicle manufacturers who require expanding driving range without adding weight. Additionally, the fairly low price of sulfur relative to materials including cobalt and nickel employed in Li-ion batteries helps in bringing down the costs of manufacturing which would subsequently decrease the energy storage system cost.
• Zinc-air Batteries
Zinc-air batteries are appealing with their lightweight construction, high energy density, and affordability. With the use of oxygen in the air as the cathode reactant and zinc as the anode, these batteries are both plentiful and friendly to the environment, as zinc is non-toxic and low-cost. They are especially ideal for hearing aid, backup power, and grid storage applications, where affordability and long-term stability are paramount.

However, their poor rechargeability and decelerated reaction kinetics are a significant drawback. Zinc deteriorates with charge-discharge cycles, shortening the battery life. Organizations such as CIC energiGUNE and others are trying to advance the rechargeability and efficiency of zinc-air batteries. For example CIC energiGUNE launched a project to conceptualize the very first electrically rechargeable zinc-air battery in order to supersede the weakness of existing non-rechargeable zinc-air batteries by developing a rechargeable type.
• Graphene-Based Batteries
Graphene batteries exploit the outstanding conductivity and mechanical resilience of graphene to boost battery performance. The batteries have the potential for charging at higher speeds along with improved energy efficiency and a longer lifespan through graphene's ability to carry electricity effectively and withstand wear and tear. The added efficiency could drastically enhance those applications with demanding power delivery speed and longevity, including consumer devices, EVs, and medical devices.

However the cost of producing graphene is high, and it is also difficult to incorporate it into existing battery technologies. Graphene-based batteries need custom manufacturing processes and materials, thus are more costly than conventional ones. Skeleton Technologies, Nanotech Energy, and other companies are working on graphene battery technology with an emphasis on scalability and minimizing costs. For instance, nanotech energy launched graphene battery production plant. This facility aims to produce high-quality graphene batteries at scale while addressing efficiency and cost concerns.
• Nuclear Power Batteries
Nuclear power batteries harness nuclear energy from isotopes to deliver a long-lasting stable power output. These batteries are invaluable for applications that require extremely long lifespans and reliability including deep-space missions where replacing batteries isn't an option. They are also used in remote power systems that can't rely on traditional power sources.

Despite their impressive longevity nuclear power batteries face challenges in terms of high production costs and regulatory hurdles due to concerns over radiation safety and handling. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce costs and improve safety measures, potentially opening doors to more terrestrial applications, such as remote sensors and backup power.
Companies such as Infinity Power, Betavolt, and others are further taking ground breaking initiatives towards nuclear battery. For example, Infinity Power, a US company, has announced a breakthrough in nuclear battery technology.
Developed with support from the US Department of Defense, their nuclear battery has demonstrated an overall efficiency of over 60%, which the company claims the highest level ever achieved compared to other radioisotope energy conversion methods. Moreover, Betavolt has introduced a nuclear battery designed to generate electricity for 50 years without needing any charging or maintenance.
• Aluminum-ion Batteries
These batteries are new alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries and they have a number of benefits that includes fast charging which is safer due to aluminum is less reactive, have a longer lifespan and high cycle stability. Aluminum is also cheap and readily available, making these batteries more cost-efficient and environmentally friendly compared to lithium-based batteries.

However, a key challenge with aluminum-ion batteries is their lower voltage output compared to Nonetheless, one major obstacle with aluminum-ion batteries is their reduced voltage output that contradicts the higher voltage output by lithium-ion batteries, restraining their energy density. Scientists are working on increasing voltage and overall efficiency to make aluminum-ion batteries commercially effective for wider applications. For instance, ACS Central Science have come up with a novel aluminum-ion (Al-ion) battery that features improved safety, recyclability, and long lifespan for large-scale energy storage applications.
Moreover, these batteries are seen as a promising solution for grid storage and portable electronics especially where fast charging and sustainability are critical. If advancements continue these batteries could become an important technology in the future of energy storage.
Conclusion
The shift from lithium-ion to next generation batteries rely on surmounting technological and scalability hurdles. Governments and private sectors are investing significantly in research and development to drive commercialization. The future battery ecosystem will probably witness a combination of these new technologies adapted to particular applications ranging from EVs and consumer electronics to grid storage and aerospace.
With increasing demand for secure and environmentally friendly energy storage technologies the battery market is on the cusp of a revolutionary change. Though lithium-ion batteries will reign supreme in the near future the aforementioned batteries are setting the stage for technology advancements that ensure greater safety and provide greener options. The next ten years will decide which of these technologies will drive the industry toward a cleaner and more energy-efficient future.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
 Mrinal Deb is a dedicated and enthusiastic researcher with two years of experience. He has closely monitored several industries, such as Tech, ICT & Media, Travel, Robotics, and Electric Vehicles. He offers valuable perspectives and analysis and enjoys sharing his insights through article writing and blogging. Outside of his professional pursuits, he enjoys reading and staying informed about industry developments. The author can be reached at [email protected]
Mrinal Deb is a dedicated and enthusiastic researcher with two years of experience. He has closely monitored several industries, such as Tech, ICT & Media, Travel, Robotics, and Electric Vehicles. He offers valuable perspectives and analysis and enjoys sharing his insights through article writing and blogging. Outside of his professional pursuits, he enjoys reading and staying informed about industry developments. The author can be reached at [email protected]
Add Comment
Related Blogs
Uncovering The Strategies of LG Energy and Others in the Battery Industry
According to NMSC analysis the battery industry valued at $1...
What Makes Tesla, ChargePoint & Siemens EV Charging Leaders?
According to NMSC analysis, the global electric vehicle (EV) charging market is...
What’s Powering the Induction Charger Revolution?
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the focus on sustainability has be...











