Exploring the Advancements of CBCT Technology
06-Dec-2024
Introduction
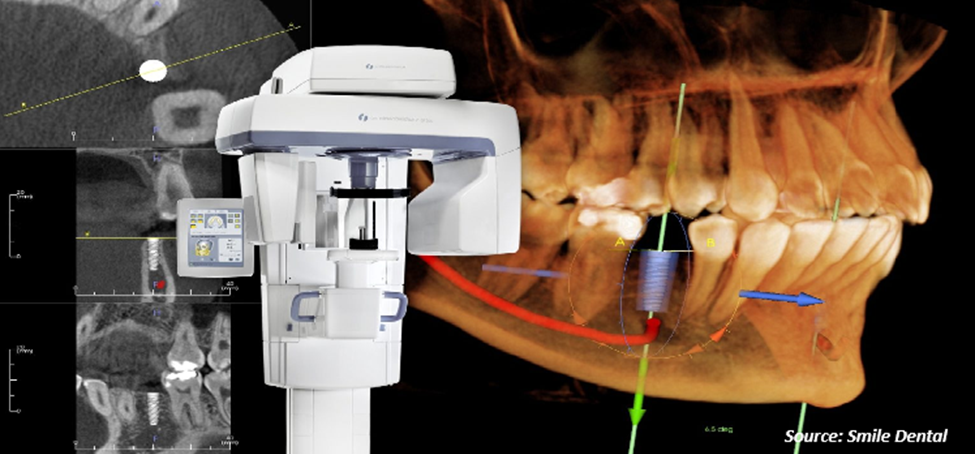
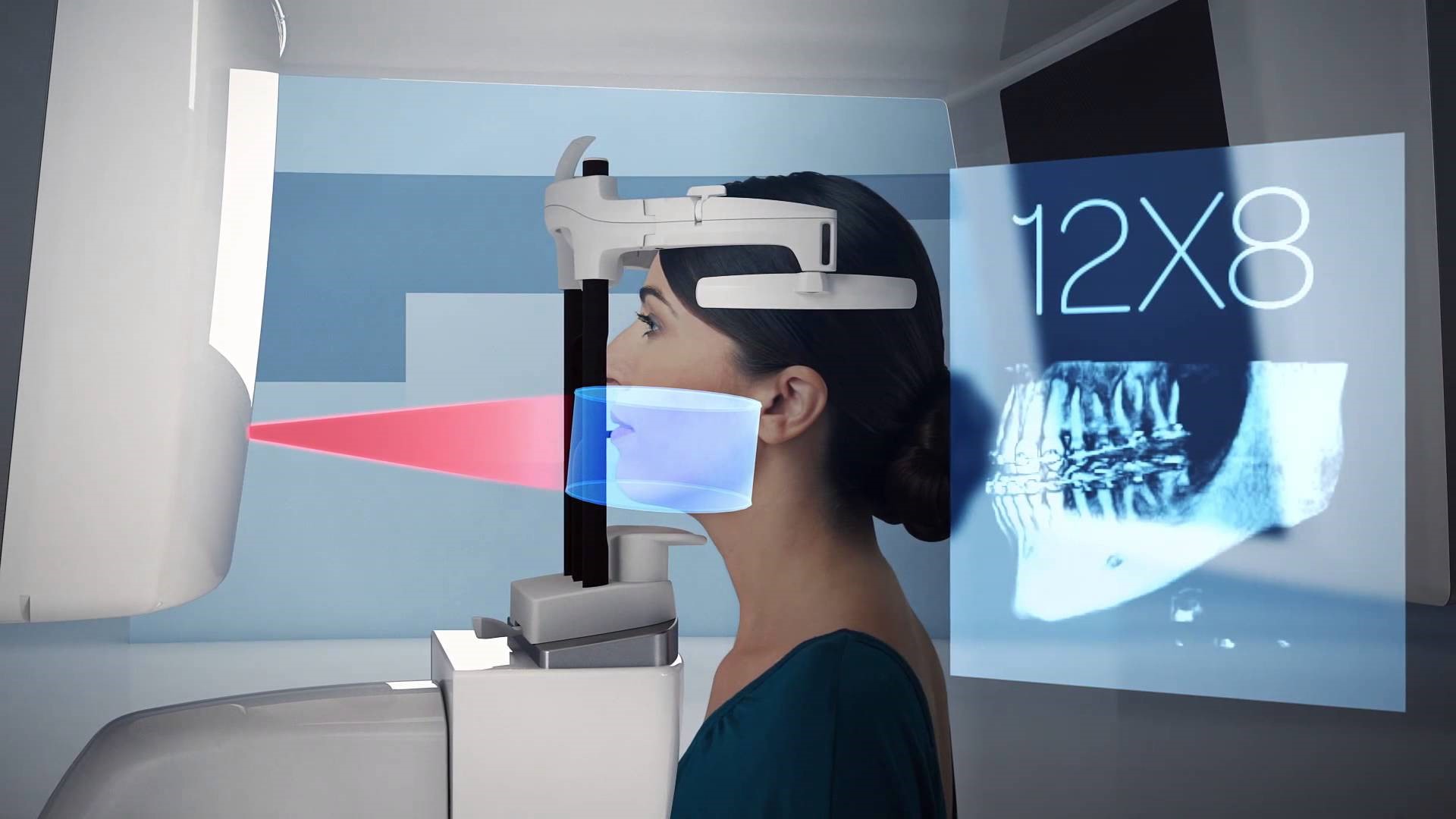
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a revolutionary imaging technology that has transformed the field of medical and dental diagnostics. By capturing 3D images of anatomical structures with a cone-shaped X-ray beam, CBCT provides detailed and comprehensive visualization, offering significant advantages over traditional imaging techniques. In this blog, we will delve into the advancements and potential of CBCT technology, highlighting its impact on various medical and dental disciplines.
Trends in CBCT Technology
The CBCT industry continues to evolve with ongoing advancements that focus on enhancing imaging quality, patient comfort, and diagnostic capabilities. Some notable advancements in CBCT technology include:
Improved Image Resolution and Dose Optimization: CBCT systems incorporate higher resolution detectors, resulting in sharper and more detailed images than before. Furthermore, there is a focus on optimizing radiation dose to minimize patient exposure while maintaining image quality. For example, Planmeca launched Planmed Verity, an improved CBCT scanner that offers enhanced image quality and reduced radiation exposure. The scanner's Ultra-Low Dose imaging protocol and CALM algorithm help minimize radiation exposure and improve image quality. These features make Planmed Verity a valuable tool for medical professionals who require high-quality imaging with minimal radiation exposure.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): The integration of AI algorithms in CBCT imaging holds great promise. AI can aid in automated image analysis, detect abnormalities, and treatment planning. It has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline workflow efficiency. For example, Planmeca introduced new AI-based tools for its Planmeca Romexis software. These tools are designed to automate tasks, improve image quality, and provide insights to help dentists and other healthcare professionals make better decisions. This tool uses AI to automatically segment soft tissues in CBCT images, making identifying and diagnosing diseases easier than before.
Mobile and Point-of-Care CBCT Systems: The development of compact and portable CBCT systems enables point-of-care imaging in various clinical settings. These mobile systems offer flexibility and convenience, particularly in emergency rooms, operating theaters, and remote locations. For example, ImageWorks, a leading provider of dental imaging solutions, launched a new turn-key mobile CBCT system called the NewTom VGi Flex. This system is a portable system that can be easily moved from one location to another, making it ideal for use in various settings. The NewTom VGi Flex features several innovative technologies designed to improve image quality and patient comfort.
Potential Innovations
The future of CBCT technology holds exciting possibilities for further advancements and innovations. Some potential advancements include:
Enhanced Soft Tissue Visualization: Researchers are working on techniques to improve the visualization of soft tissues using CBCT. This can open new avenues for diagnosing and monitoring conditions, such as tumors, vascular malformations, and inflammatory processes. For example, Philips introduced SmartCT, a new soft tissue imaging technology that uses advanced algorithms to enhance the contrast and clarity of soft tissue images. This makes it easier to identify and diagnose diseases. SmartCT also received FDA 510(k) clearance and includes software applications for angiography, neurology, soft-tissue imaging, and guidewire/catheter navigation. It is a significant advancement in medical imaging technology, providing enhanced image quality and improving diagnostic accuracy for soft tissue imaging.
Real-time Imaging and Dynamic CBCT: Real-time imaging capabilities and dynamic CBCT are emerging areas of research. These technologies would enable the visualization of dynamic processes, such as joint movements, cardiac motion, or swallowing. They provide valuable insights for diagnosis and treatment planning. For example, Brainlab launched a new real-time monitoring system called ExacTrac Infrared Monitoring based on CBCT technology to track patient positioning during radiation therapy. The system uses infrared cameras to track the patient's movement and adjust the radiation beam in real time.
Fusion with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): The fusion of CBCT with AR and VR technologies holds tremendous potential. It can provide surgeons and dentists with immersive visualization, facilitating precise interventions, implant placements, and orthognathic surgeries. For example, Apoqlar, a German medical technology company, received FDA clearance for its mixed reality surgical planning platform, VSI HoloMedicine. The platform allows surgeons to visualize and plan complex procedures using 3D holographic images.
Conclusion
CBCT has revolutionized medical and dental diagnostics by capturing 3D images of anatomical structures with a cone-shaped X-ray beam. The advancements in CBCT technology have led to improved imaging quality, patient comfort, and diagnostic capabilities. With higher-resolution detectors and optimized radiation doses, CBCT provides sharper and more detailed images than before while minimizing patient exposure. The integration of AI algorithms enhances image analysis, detection of abnormalities, and treatment planning. This, in turn, improves diagnostic accuracy and workflow efficiency.
The development of compact and portable CBCT systems enables point-of-care imaging in various clinical settings, offering flexibility and convenience. Exciting future directions include enhanced visualization of soft tissues, real-time imaging, dynamic CBCT, and fusion with augmented reality and virtual reality technologies for immersive surgical planning. CBCT continues to shape the future of healthcare, providing valuable insights for precise interventions, implant placements, and orthognathic surgeries. This is expected to ultimately improve patient care and treatment outcomes.
About the Author
 Shyam Gupta is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with more than four years of experience. He assists clients in overcoming difficult business challenges by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. He has been closely monitoring a number of industries, such as Medical Devices, Healthcare IT, and Biotechnology & Diagnostics. He has a keen interest in writing articles and uses blogs as a medium to share his thoughts. He spends his time reading and painting, when not keeping up with industry news. The author can be reached at info@nextmsc.com
Shyam Gupta is a passionate and highly enthusiastic researcher with more than four years of experience. He assists clients in overcoming difficult business challenges by providing actionable insights through exhaustive research. He has been closely monitoring a number of industries, such as Medical Devices, Healthcare IT, and Biotechnology & Diagnostics. He has a keen interest in writing articles and uses blogs as a medium to share his thoughts. He spends his time reading and painting, when not keeping up with industry news. The author can be reached at info@nextmsc.com
Add Comment
Related Blogs
Role Of Companies In Shaping The Blood Gas And Electrolyte Analyzer Market
According to Next Move Strategy Consulting, the global blood...
Analysis of Key Players Operating in the Global Surgical Instrument Industry
Next Move Strategy Consulting forecasts more than 1.7-fold g...
CBCT Industry Is Dominated By Dentsply Sirona, Philips, & Vatech With More Than 45% – Know Why
Next Move Strategy Consulting predicts a significant growth...